3. Líneas y curvas
Líneas
Para dibujar líneas con canvas se utilizan los siguientes métodos:
- beginPath(): Método para declarar que estamos a punto de trazar un nuevo camino.
context.beginPath();
- moveTo(): Posicionar el punto de comienzo.
ctx.moveTo(10,10);
- lineTo(): Dibujar la línea recta desde la posición inicial hasta la nueva posición.
ctx.lineTo(190,90);
- stroke(): Dibujar la línea, hacerla visible. A menos que se especifique, el color por defecto es negro.
ctx.stroke();
- lineWidth: Establecer un ancho a la línea.
ctx.lineWidth = 10;
- strokeStyle: Establecer un color.
ctx.strokeStyle = '#FF5733';
- lineCap: Establecer un formato para el tope de la línea, pueden ser: 'butt', 'round' y 'square' (extremo, redondo o cuadrado).
ctx.lineCap ='round'
Estas propiedades se deben establecer antes de llamar a stroke().
En el siguiente código se aplican las funciones anteriores:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<canvas id="myCanvas" width="200" height="100" style="border:1px solid #d3d3d3;">
<script>
//Inicializar el elemento canvas.
var c=document.getElementById("myCanvas");
var ctx=c.getContext("2d");
ctx.moveTo(10,10);
ctx.lineTo(190,90);
ctx.lineWidth = 10;
ctx.strokeStyle = '#FF5733';
ctx.lineCap ='round'
ctx.stroke();
</script>
</body>
</html>
Elemento canvas:

Curvas
Arco
- arc(): Los arcos se definen por un punto central, un radio, un ángulo inicial, un ángulo final y la dirección de dibujo. Los arcos se pueden diseñar con las propiedades lineWidth, strokeStyle y lineCap.
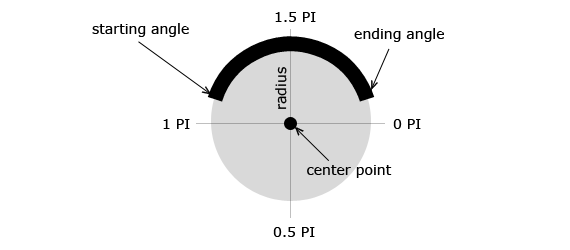
Ejemplo 1:
Para crear una curva hemos establecido el ángulo de inicio en 0 y el ángulo final en 2 * Math.PI.
Los parámetros x,y definen las coordenadas x,y del centro del círculo.
El parámetro r define el radio del círculo.
ctx.arc(x,y,r,angulo_inicio,angulo_fin)
ctx.arc(50,50,40,0,2*Math.PI);
Ejemplo 2:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="myCanvas" width="578" height="250"></canvas>
<script>
var canvas = document.getElementById('myCanvas');
var ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
var x = canvas.width / 2;
var y = canvas.height / 2;
var radius = 75;
var startAngle = 1.1 * Math.PI;
var endAngle = 1.9 * Math.PI;
var counterClockwise = false;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(x, y, radius, startAngle, endAngle, counterClockwise);
ctx.lineWidth = 15;
ctx.strokeStyle = '#FF5733';
ctx.lineCap ='round'
ctx.stroke();
</script>
</body>
</html>

Curva cuadrática
- quadraticCurveTo(): Las curvas cuadráticas se definen por el punto medio, un punto de control y un punto final. Las curvas cuadráticas se pueden diseñar con las propiedades lineWidth, strokeStyle y lineCap.
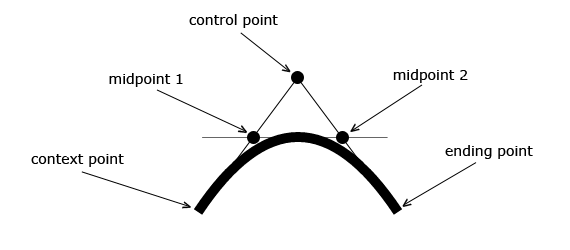
Ejemplo:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<canvas id="myCanvas" width="578" height="200"></canvas>
<script>
var canvas = document.getElementById('myCanvas');
var ctx = canvas.getctx('2d');
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(188, 150);
ctx.quadraticCurveTo(288, 0, 388, 150);
ctx.lineWidth = 10;
// line color
ctx.strokeStyle = '#FF5733';
ctx.lineCap ='round'
ctx.stroke();
</script>
</body>
</html>
