Express
Tutorial de Express
- Home page
- Installing
- Hello world!
- Express application generator
- Basic routing
- Static Files
- Repo hello-express
- Repo basic-routing-express
Ejemplos sencillos
- El repositorio hello-express
- Ejemplos de routing
- Following the tutorials at express.com
- JS and express.js example of how to load the contents of a file inside a textarea tag
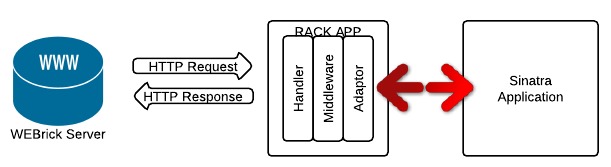
Middlewares
Express is a routing and middleware web framework that has minimal functionality of its own: An Express application is essentially a series of middleware function calls.
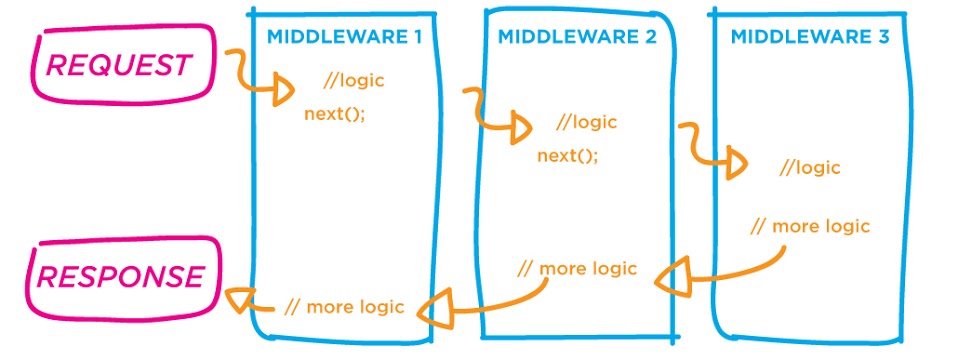
Middleware functions are functions that have access to the request object (req), the response object (res), and the next middleware function in the application’s request-response cycle. The next middleware function is commonly denoted by a variable named next.
The Request Object
The req object represents the HTTP request and has properties for the request query string, parameters, body, HTTP headers, and so on.
app.get('/user/:id', function(req, res) {
res.send('user ' + req.params.id);
});
Sirviendo varias rutas con un solo middleware
En Express es posible servir varias rutas en un sólo middleware
usando la notación :string_sin_dos_puntos. En ese
caso la correspondiente cadena queda en req.params:
// Supongamos que se visita con GET la ruta /usuario/pepe
app.get('/usuario/:id', function (req, res) {
console.log(req.params); // { id: "pepe" }
res.send('USUARIO: '+(req.params.id || 'unknown' )); // USUARIO: pepe
});
Cuando se visita /usuario/pepe el valor de req.params.id
será pepe.
Es posible también usar una expresión regular para limitar el matching:
// Supongamos que se visita con GET la ruta /mongo/input1.csv
get('/mongo/:ejemplo([a-zA-Z_]\w*\.csv)', function(req, res) {
console.log(req.params.ejemplo); /* input1.csv */
/* ... Consultar la base de datos y retornar contenidos de input1.csv ... */
});
There's another way to do this.
We can execute a function for a specific parameter before a route function executes.
Let's rewrite our previous example using app.param.
app.param('ejemplo', function (req, res, next, ejemplo) {
if (ejemplo.match(/^[a-z_]\w*\.csv$/i)) {
req.ejemplo = ejemplo;
} else {
next(new Error(`<${ejemplo}> does not match 'ejemplo' requirements`));
/* Error: <input1.csx> does not match 'ejemplo' requirements at app.js:85:12 */
}
next();
});
// Supongamos que se visita con GET la ruta /mongo/input1.csv
app.get('/mongo/:ejemplo', function(req, res) {
console.log(req.params.ejemplo); /* input1.csv */
console.log(req.ejemplo); /* input1.csv */
/* ... Consultar la base de datos y retornar contenidos de input1.csv ... */
});
app.paramis an amazing function and can be really handy for checking or parsing parameters.Remember to pass the parameter as 4th function parameter though!
next()is a function passed as third parameter to a route / param function.- When executed it will take you to the next middleware / route.
- If you give
nexta parameter such asnew Error()or just a string, it will show the user an error.
Para mas detalles sobre routing estudie los ejemplos de routing en Express en este repo.